Compiling Linux Kernel and Add Custom System Calls
- Assignment 1: Compiling Linux Kernel and Adding Custom System Calls
- Compiling Linux Kernel
Change kernel suffix
- Adding custom system calls
sys_hellosys_revstr
- Compiling Linux Kernel
Part 1: Compiling Linux Kernel & Change kernel suffix
Step 1: Download and Extract the Linux kernel source code
1 | wget https://cdn.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/linux-5.19.12.tar.xz |
1 | tar -xJf linux-5.19.12.tar.xz |
1 | cd linux-5.19.12 |
Step 2: Install essential tools and libraries required for compiling the kernel
1 | sudo apt update |
Step 3: Copy current kernel config file, then set it as default configuration
1 | cp /boot/config-`uname -r`* .config |
1 | make defconfig |
Step 4: Modify the config file
1 | vim .config |
Find CONFIG_LOCALVERSION change value to -os-312551002
Step 5: Compile the kernel (wait 20~50 mins)
1 | make -j4 |
Step 6: Install the kernel modules
1 | sudo make modules_install install |
Step 7: Update GRUB, the bootloader
1 | sudo update-grub2 |
Step 8: Reboot the system
1 | reboot |
Press Esc button when system boot > Advanced options for Ubuntu > choose Linux 5.19.12-os-312551002 to start
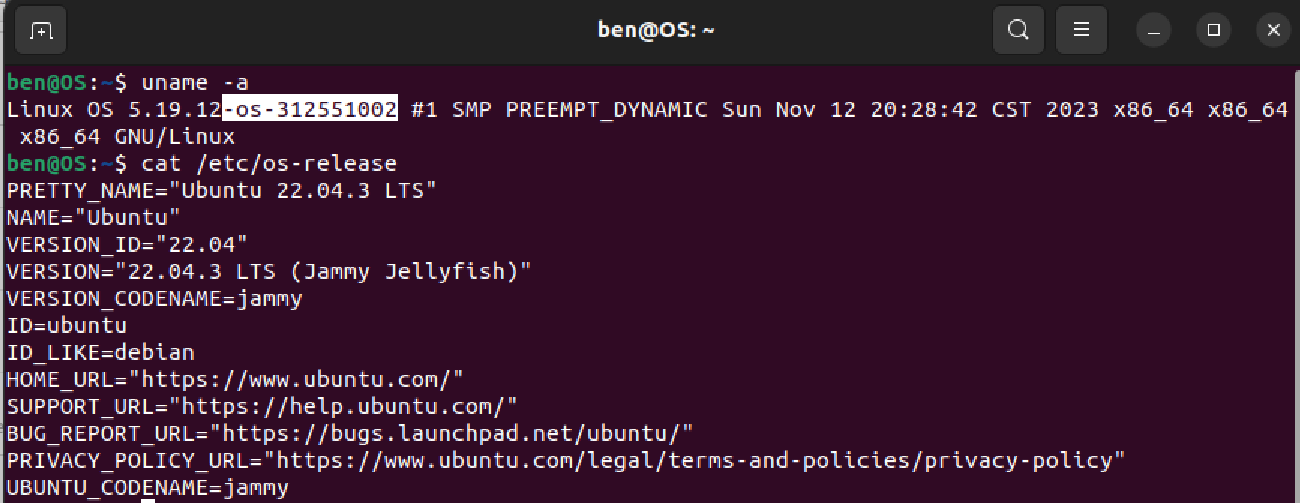
Step 9: Check the running kernel version
1 | uname -a |
The screenshot of changed kernel suffix
Part 2: Adding custom system calls
sys_hello
For the implementation of the sys_hello system calls, I modified 4 kernel source files and added 1 new C code to verify if the system calls work correctly. The modified and added files are:
- linux-5.19.12/kernel/sys.c
- linux-5.19.12/arch/x86/include/generated/uapi/asm/unistd_64.h
- linux-5.19.12/arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl
- linux-5.19.12/include/linux/syscalls.h
- sys_hello.c
Step 1: In the sys.c file, add the following code to defines a new system call named “hello”.
1 | SYSCALL_DEFINE0(hello){ |
Step 2: In the unistd_64.h file, add the following code to defines the system call number for “hello”.
1 | #define __NR_hello 548 |
Step 3: In the syscall_64.tbl file, add the following entry to map system call number to its corresponding function.
1 | 548 common hello sys_hello |
Step 4: In the syscalls.h file, add the following code to add the new system call in the header file.
1 | asmlinkage long sys_hello(void); |
Step 5: Create new C code file named sys_hello.c and add the following code:
1 |
|
Step 6: Rebuild the kernel to compile the modified kernel source code.
1 | make |
Step 7: Reinstall the kernel
1 | sudo make modules_install install |
Step 8: Reboot the kernel
1 | reboot |
Step 9: Compile the sys_hello.c file to test if the system call operates correctly.
1 | gcc sys_hello.c -o sys_hello |
1 | ./sys_hello |
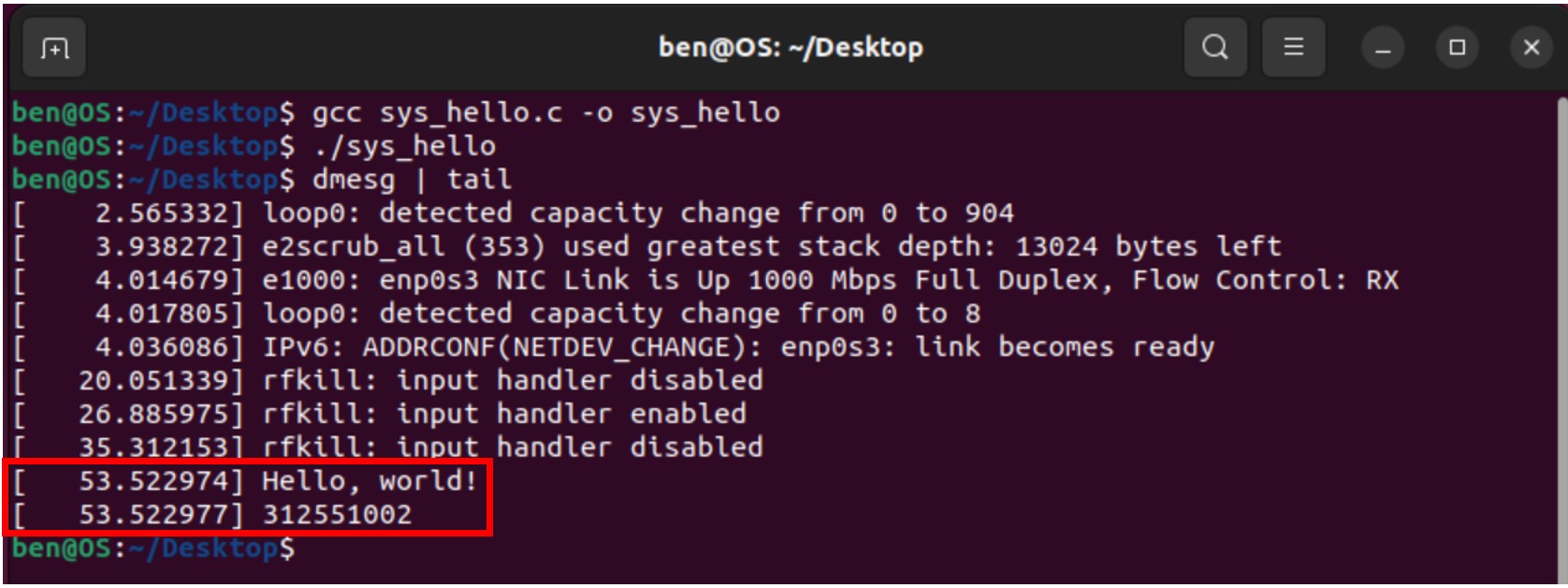
Step 10: Display the output messages produced by the sys_hello system call.
1 | dmesg | tail |
The screenshot of the results of executing sys_hello system call:
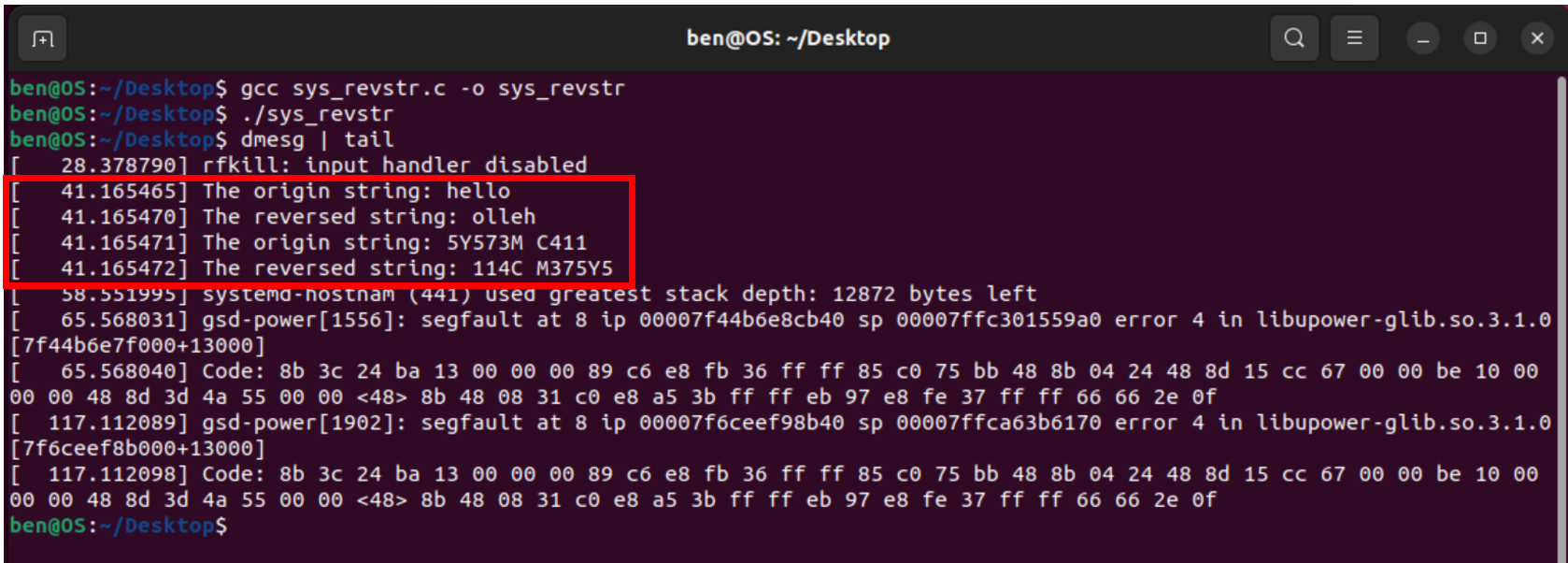
sys_revstr
For the implementation of the sys_hello system calls, I modified 4 kernel source files and added 1 new C code to verify if the system calls work correctly. The modified and added files are:
- linux-5.19.12/kernel/sys.c
- linux-5.19.12/arch/x86/include/generated/uapi/asm/unistd_64.h
- linux-5.19.12/arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl
- linux-5.19.12/include/linux/syscalls.h
- sys_revstr.c
Step 1: In the sys.c file, add the following code to defines a new system call named “revstr”.
1 | SYSCALL_DEFINE2(revstr, int, len, char __user *, usr_str) { |
Step 2: In the unistd_64.h file, add the following code to defines the system call number for “revstr”.
1 | #define __NR_revstr 549 |
Step 3: In the syscall_64.tbl file, add the following entry to map system call number to its corresponding function.
1 | 549 common revstr sys_revstr |
Step 4: In the syscalls.h file, add the following code to add the new system call in the header file.
1 | asmlinkage long sys_revstr(int len, char __user *usr_str); |
Step 5: Create new C code file named sys_revstr.c and add the following code:
1 | #include <assert.h> |
Step 6: Rebuild the kernel to compile the modified kernel source code.
1 | make |
Step 7: Reinstall the kernel
1 | sudo make modules_install install |
Step 8: Reboot the kernel
1 | reboot |
Step 9: Compile the sys_revstr.c file to test if the system call operates correctly.
1 | gcc sys_revstr.c -o sys_revstr |
1 | ./sys_revstr |
Step 10: Display the output messages produced by the sys_ revstr system call.
1 | dmesg | tail |
The screenshot of the results of executing sys_ revstr system call: